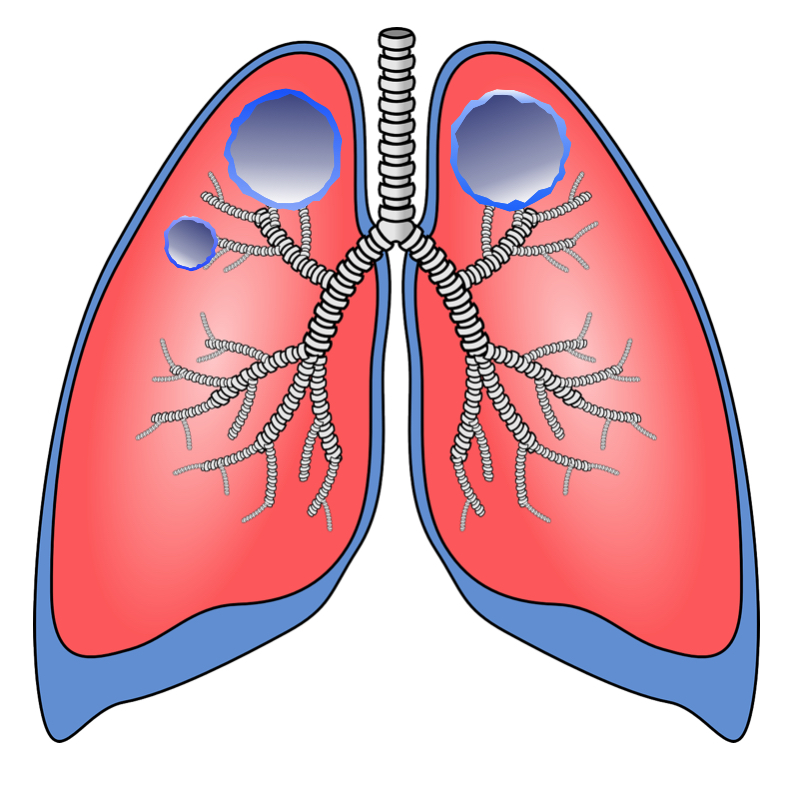
Permanent enlargement of the bronchus is called bronchiectasis. In bronchiectasis, there is usually also destruction of the bronchial wall. There are types of bronchiectasis such as cylindrical, cystic and saccular.
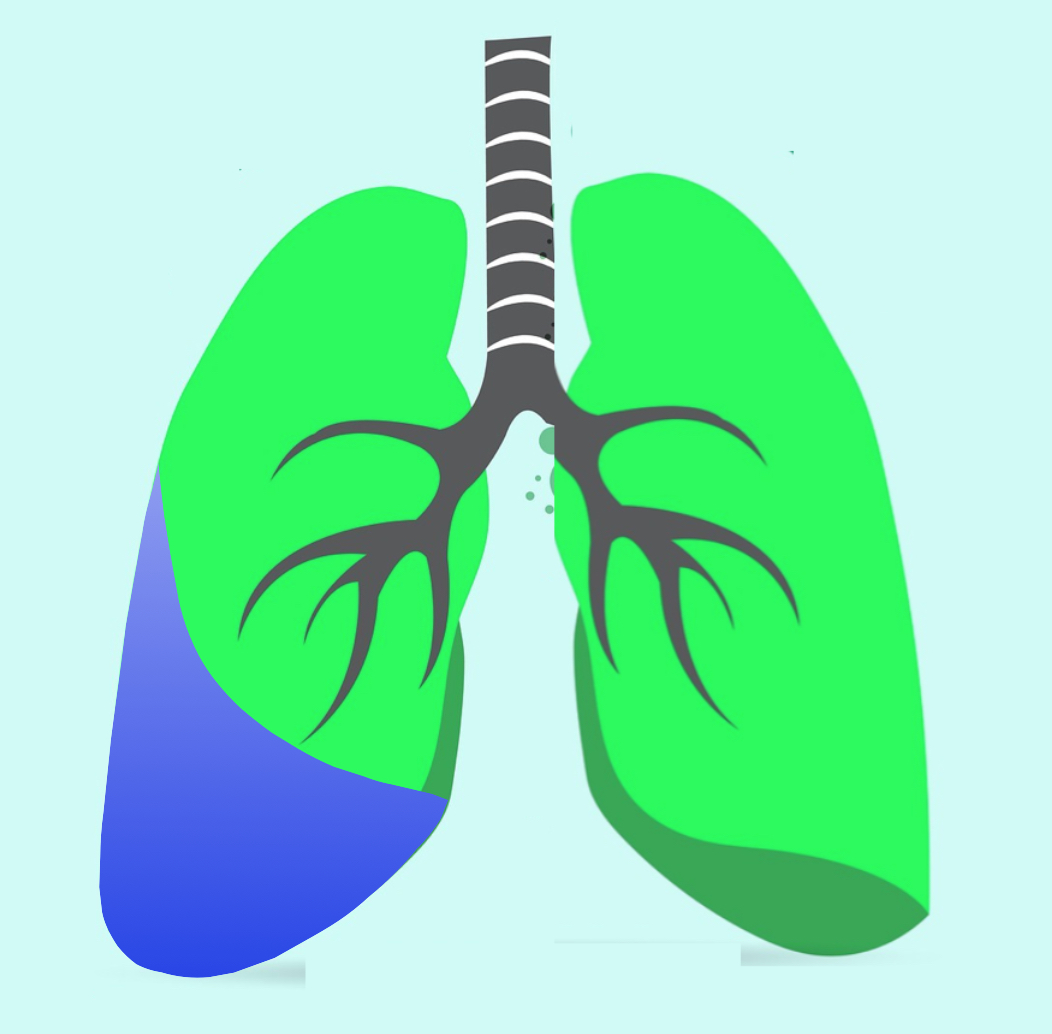
Pleural effusion (PE) is the collection of fluid between the lung membranes (pleura). There are two membranes that surround the lungs. The membrane just outside the lung is called the visceral pleura, and the membrane just below the rib cage is called the parietal pleura.
The disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex is called tuberculosis disease or shortly tuberculosis. The main mode of transmission of tuberculosis is airborne transmission. There is a cure for all drug-sensitive forms of tuberculosis.
Image: Pexels
What is Sars-Cov-2?
The virus that causes Covid-19 is called Sars-Cov-2 virus.
How does Sars-Cov-2 virus enter the cell?
Sars Cov-2 virus binds to the ACE-2 receptors on the cell with the receptor binding domain of the spike protein, then enters the cell and begins to multiply. By blocking the region of the virus that binds to the ACE-2 receptor, the binding of the virus to the cells, and thus the entry of the virus into the cell can be prevented.profdromerdeniz.com
What is Coronavac (Sinovac) vaccine?
Coronavac (sinovac) is an inactivated virus vaccine. Sars-Cov-2 virus produced/replicated in Vero cells is condensed and purified after chemical inactivation with β-propiolactone, and then passed through a series of processes to become an inactivated vaccine. In the inactivated vaccine, there are other antigens of the virus as well as spike protein antigens. profdromerdeniz.com. Since there is no live virus in the inactivated vaccine, it does not cause a viral disease. After this vaccine is administered, mainly humoral immunity (immunity with antibody production) is formed against the antigens in the vaccine. There is little or no cellular immunity (absence of antibodies, predominant macrophage and T-cell immunity) against inactivated vaccines. profdromerdeniz.com
According to the results of the Phase1/2 clinical trial, it was reported that individuals who received the Coronovac vaccine had lower levels of antibody production compared to the antibody levels formed in individuals who had had Covid-19 disease. The protection of Coronavac against the Covid-19 infection caused by original Sars-Cov-2 virus (with no significant mutations) was reported between 50.7% and 84%. profdromerdeniz.com
What is Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine?
The Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, an mRNA vaccine, carries the code for the receptor binding domain antigen of the spike protein of Sars Cov-2 virus. The vaccine can be described roughly as that it consists of modified mRNA that carries the code for the spike protein receptor binding domain antigen surrounded by lipid nanoparticles. profdromerdeniz.com. After vaccination, the vaccinated individual’s own cells produce the receptor binding site antigen of the spike protein of Sars Cov-2 virus. This antigen is not a virus, just a small part of the virus. Therefore, it does not cause a viral disease. However, since it is a foreign substance to the human body, both humoral immunity and cellular immunity are formed against this antigen. Since mRNA itself is also recognized as a pathogen by cells, it stimulates a strong immunity.
It has been reported that Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine prevents Covid-19 infection caused by the original Sars-Cov-2 virus (with no significant mutations) by 95% in individuals aged 16 years and older who have not been infected with Sars-Cov-2 virus before.
Is the protection of Covid-19 vaccines permanent?
Immunity against Sars-Cov-2 virus in those who have had Covid-19 disease or who have been vaccinated decreases over time. Antibody levels against Sars-Cov-2 virus decrease as the time passes after getting sick or getting vaccinated. Furthermore, the Sars-Cov-2 virus is a frequently mutating virus. In other words, there may be changes in the antigenic properties of the virus. This situation reduces the protective effectiveness of antibodies caused by vaccine or disease. profdromerdeniz.com
Being immune or vaccinated against the virus due to the above-mentioned reasons may not prevent anyone from becoming Covid-19 again. Since the antibody levels formed in individuals vaccinated with inactivated virus vaccines are relatively much lower, the protection is greatly reduced or lost as the time elapses after the vaccine is administered. profdromerdeniz.com
The Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine continues to provide significant protection against mutated viruses, as it generates a very high rate of antibodies against the Sars-Cov-2 virus. However, it is observed that the protection against the Delta variant, which is still the most common variant in circulation, is considerably lower than the protection against the original Sars-Cov-2 virus (with no significant mutations) in individuals who have passed a long time after the second dose of vaccine. This is particularly evident in older individuals. profdromerdeniz.com
Legal Disclaimer: The medical information on this website can only be considered as a source of information, cannot be considered as any medical advice, cannot be used for any diagnosis or treatment purposes, or this information cannot be relied upon for diagnosis or treatment purposes. The medical information on this website is not intended for patient education and cannot create a patient doctor relationship. Please consult your doctor for any health-related decision or medical advice. profdromerdeniz.com
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a disease characterized by the hardening and loss of elasticity of the lungs, a condition in which there is an increase in connective tissue in the lungs called fibrosis. This increase in connective tissue disrupts the structure of the lung tissue. Thorax HRCT is the most important test for the diagnosis. Pulmonary function tests show a restrictive pattern. There is no cure for the disease.
COPD is a progressive lung disease characterized by irreversible airway obstruction. COPD is usually caused by prolonged exposure to smoke, harmful dust or chemicals, mainly cigarette smoke. Exposure to biomass (wood, manure, etc.) smoke for a long time is also considered among the causes of COPD.
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is the inflammation of the lung tissue caused by microorganisms. Mainly bacteria and viruses cause pneumonia, fungi can also cause pneumonia in immunocompromised patients.profdromerdeniz.com.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Symptoms of pneumonia are cough, sputum, chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, fever, sweating, chills, loss of appetite, weakness and malaise. Confusion and disorientation may also be observed, especially in elderly patients. Patients with pneumonia are not always expected to have all symptoms. Pneumonia may occur with a picture in which respiratory system symptoms such as cough, sputum, and shortness of breath are dominant, and in some patients, weakness, malaise and fever may be the initial symptoms. profdromerdeniz.com.
How is pneumonia diagnosed?
The diagnosis of pneumonia is made by physical examination, chest radiograph, and, if necessary, computed tomography of the thorax. In lung listening (auscultation) of patients with pneumonia, abnormal breathing sounds called crepitant rales are heard, but crepitant rales may not always be heard depending on the location and size of the involvement in the lung. profdromerdeniz.com.
In addition, a bronchial breathing sound is heard in fewer cases. Absence of physical examination findings does not mean that there is no pneumonia. In addition, pneumonia-specific findings are observed on chest X-ray. profdromerdeniz.com. Lungs, which are airy tissue, can be observed in a color close to black radiologically, while pneumonic areas can be observed near white or in shades of gray. A normal chest X-ray does not mean that there is no pneumonia. Computed tomography of thorax can be performed in order to confirm the diagnosis in patients with normal chest X-ray whose findings are suspected to have pneumonia. profdromerdeniz.com.
How is pneumonia treated?
Depending on the clinical, radiological and other laboratory characteristics of the patients, it is decided whether they will be treated on an outpatient basis, in the hospital or in the intensive care unit. Pneumonia treatment is done empirically, since the causative microorganism(s) cannot be detected in approximately 50% of the cases, even with advanced examinations including bronchoscopic methods, the isolation of the agent takes time, and the possible microorganisms are predicted according to the location and conditions of the pneumonia. In other words, at the beginning of the treatment in outpatients, no examination is made for the causative agent, and antibiotic treatment is given for possible microorganisms. Pneumonia treatment is not only antibiotic therapy, but supportive treatment including proper hydration and rest is also necessary. profdromerdeniz.com. Advanced tests and oxygen therapy may be required in hospitalized patients. Severe respiratory failure may develop in some patients with pneumonia, so these patients are treated in the intensive care unit with ventilator support. Pneumonia is a disease with high mortality in the elderly (and those with concomitant chronic diseases). Pneumonias of patients with suppressed immune system should be treated in advanced centers because their mortality may be high and special methods may be required for diagnosis. profdromerdeniz.com.
Legal Disclaimer: The medical information on this website can only be considered as a source of information, cannot be considered as any medical advice, cannot be used for any diagnosis or treatment purposes, or this information cannot be relied upon for diagnosis or treatment purposes. The medical information on this website is not intended for patient education and cannot create a patient doctor relationship. Please consult your doctor for any health-related decision or medical advice. profdromerdeniz.com
Spirometry is an extremely easy to perform pulmonary function test to be used to measure lung volumes, capacities and respiratory flow rates.